You critically need high-durability fastening solutions for modern applications. The industrial fastening market exceeded USD 99 billion in 2024. Self-locking stainless steel cable ties provide the definitive answer to this critical demand. Their superior performance over traditional alternatives drives their rising global demand, with the Stainless Steel Cable Ties market projected to grow at a 5.4% CAGR.
Key Takeaways
- Self-locking stainless steel cable ties last longer. They work better than plastic ties in tough places. They resist heat, cold, and chemicals.
- These ties save money over time. They need fewer replacements. This means less work and fewer stops in operations.
- You can use stainless steel ties in many places. They work in energy, marine, and car industries. They keep things secure and safe.
Why Industries Are Shifting: The Limitations of Traditional Fastening

You understand the critical need for reliable fastening. For years, industries relied on conventional solutions. However, these traditional options often fall short in demanding environments. You need to recognize their inherent weaknesses to appreciate the revolution self-locking stainless steel cable ties bring.
The Vulnerabilities of Plastic Cable Ties
Plastic cable ties, particularly those made from nylon, appear convenient and cost-effective at first glance. Yet, their vulnerabilities become glaringly obvious in industrial applications. A significant failure point, accounting for over 80% of failures, involves the release of the pawl. This small component in the tie’s head must remain flexible for installation but stiff enough to secure the load. Environmental factors like heat, moisture, chemical exposure, and UV light severely compromise the pawl’s performance. This leads to stress cracking, material degradation, and ultimately, failure.
You also encounter common mistakes that lead to plastic tie failures. Pulling a tie too tightly can cut into wire insulation, causing damage or shorts. It can also restrict airflow, leading to overheating in electrical applications. Using the wrong type of cable tie is another frequent error; basic nylon ties quickly fail outdoors due to sunlight exposure. You must select specific ties for UV resistance, flame retardancy, or metal composition for certain applications. Leaving sharp edges after cutting also poses a risk, potentially scratching skin or damaging nearby cables. Furthermore, regular nylon ties degrade and become brittle when exposed to UV rays over time, making indoor ties unsuitable for outdoor use. Poor cable management planning also leads to tangled cables, stress on connectors, and difficulty tracing wires, potentially causing equipment damage or electrical issues. You also find that cheap, brittle ties made from low-quality materials quickly fail under tension or heat.
The root causes of nylon tie breakage stem from several areas. The quality of the raw material itself plays a crucial role. Using recycled or poor-quality PA66 leads to an uneven molecular structure, reducing strength and durability. Incorrect material moisture content also impacts performance; too dry leads to brittleness, while too wet reduces strength. Uneven distribution or imbalanced ratios of additives (for weathering, flame retardancy, flexibility) create local strength weaknesses. The production process also influences durability. Incorrect temperature, pressure, or cooling speed during injection molding degrades the material or results in insufficient molding, leading to weak products. Poor mold design, such as too thin teeth or sharp corners, creates stress concentrations. Omitting post-molding steps like boiling or humidification leaves ties brittle due to over-drying. Finally, structural and design issues contribute to breakage. Improper design of teeth, locking clips, or the tie body (e.g., too thin body, too dense/sparse teeth, weak latches) leads to failure. You must consider specific design requirements for different applications, such as high/low temperature resistance and UV resistance for automotive ties, or flame retardancy for electrical ties.
Common failure modes of plastic cable ties in industrial applications include:
- Material-Related Failures: You experience low tensile strength and brittleness, often due to recycled or inferior polymer blends. This leads to fractures, especially in cold temperatures (e.g., below -20°C). Poor locking mechanism design, such as traditional single-tooth structures, also loosens under vibration or repeated stress.
- Environmental Degradation: UV and weathering damage from prolonged sunlight exposure causes surface cracking, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties. Hydrolysis in humid conditions, where nylon absorbs moisture, leads to brittleness or reduced tensile strength. Thermal instability is also a concern, as extreme heat causes softening, deformation, or melting, while freezing temperatures make ties brittle.
- Installation and Usage Errors: Over-tightening creates stress concentrations and premature failure, or restricts airflow around cables. Incorrect storage practices, such as exposure to direct sunlight, high temperatures, or moisture, degrade ties before use. Reusability limitations also exist, as repeatedly opening and closing standard ties damages the locking mechanism.
- Seasonal and Regional Challenges: You observe winter brittleness in cold climates due to low humidity and reduced molecular mobility. Coastal and marine environments also present challenges with corrosion, weakening the material.
Consider the typical lifespan differences. While UV-resistant nylon cable ties can serve short-term outdoor needs, they begin degrading in as little as 1–2 years depending on sun exposure. For long-term, critical installations where failure is not an option, stainless steel is the dependable, expert-recommended choice. Stainless steel is completely immune to UV damage, ensuring outdoor installations remain secure for years, whereas UV rays destroy plastic cable ties within months. Stainless steel cable ties maintain strength from -80°F to 1000°F, suitable for arctic to desert conditions. Plastic ties become brittle in cold and soften in heat. Stainless steel resists virtually all chemical attacks from acids, bases, and solvents common in industrial environments, which can dissolve plastic ties. Stainless steel’s superior tensile strength allows it to handle dynamic loads without degrading from vibration and repeated movement, which cause plastic ties to fatigue and fail.
You can see the stark contrast in expected lifespans:
| Type of Cable Tie | Typical Lifespan (Years) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Decades | Ideal for extreme conditions; corrosion-resistant. |
| Nylon (indoor) | 5-10 | Commonly used. |
| Nylon (outdoor) | 1-2 | Lifespan reduced outdoors without UV protection. |
| UV-Resistant Nylon | 5-7 | Made for outdoor use; protects against UV damage. |
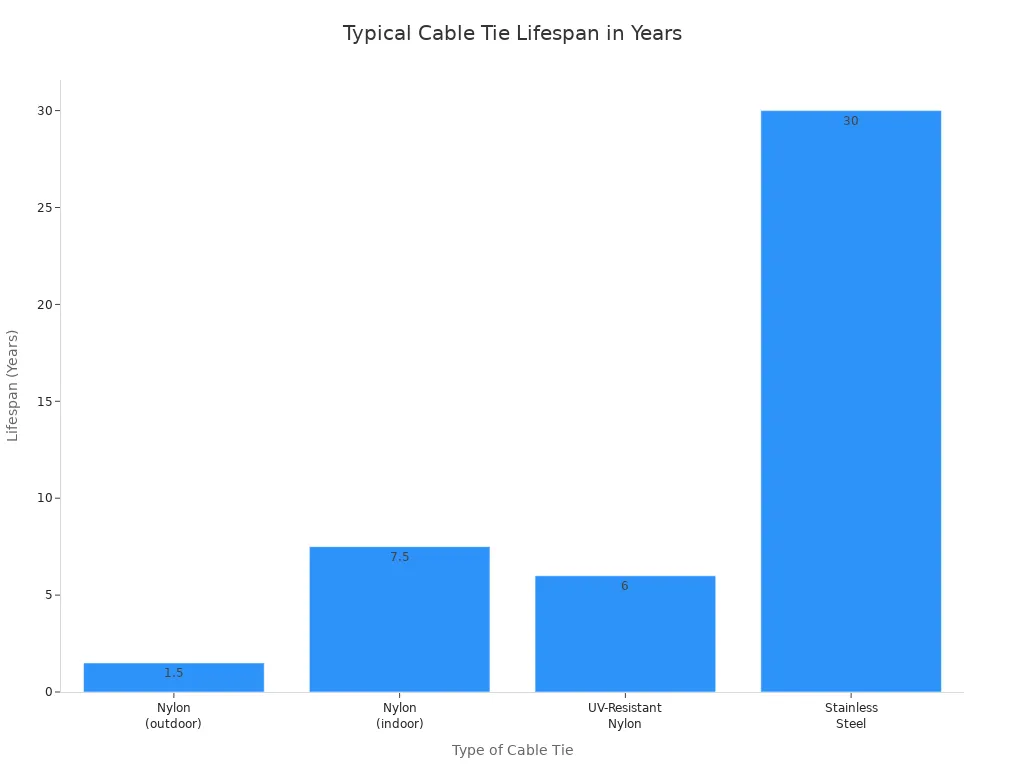
In a refinery complex with a highly corrosive atmosphere, switching from plastic to stainless steel cable ties significantly increased durability. Stainless steel ties are expected to last up to five years, greatly exceeding the six-month lifespan of plastic alternatives. This is due to their high tensile strength and resistance to heat, ensuring secure cable fastening even under severe temperature variations. Furthermore, stainless steel cable ties excel in outdoor environments due to their UV resistance, lasting from 10 to 30 years, unlike nylon ties which can degrade within months.
Shortcomings of Other Metal Fasteners
While you might consider other metal fasteners like galvanized steel or aluminum, they also present significant limitations compared to stainless steel cable ties.
Galvanized steel, for instance, receives a zinc coating to protect against rust. However, this coating wears away over time, potentially exposing the underlying steel core to corrosion. In contrast, stainless steel’s rust protection is inherent throughout the entire material due to its composition, which includes at least 10% chromium. This provides consistent, long-term corrosion resistance you cannot achieve with a mere coating.
You also find a notable difference in strength. Compare the typical tensile and yield strengths:
| Material | Tensile Strength (PSI) | Yield Strength (PSI) |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 100,000 – 150,000 | 30,000 – 40,000 |
| Galvanized Steel | 38,000 – 62,000 | 21,000 – 31,000 |
Stainless steel clearly offers superior mechanical properties, providing a much stronger and more reliable fastening solution.
When you consider aluminum, you face the challenge of galvanic corrosion. If you use aluminum to attach a large sheet of stainless steel, the aluminum’s lifespan significantly reduces due to this electrochemical reaction. Experts advise using neoprene EPDM or bonding washers as a barrier between stainless steel fasteners and aluminum materials to prevent this type of corrosion. This adds complexity and cost to your installation, which you avoid with an all-stainless steel solution. These limitations highlight why industries increasingly turn to the inherent advantages of self-locking stainless steel cable ties.
Unpacking the Superiority of Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You understand the limitations of traditional fasteners. Now, you need to explore why self-locking stainless steel cable ties represent a significant leap forward. These innovative solutions offer unparalleled advantages, making them the preferred choice for critical applications worldwide.
Unmatched Durability and Longevity of Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You demand fasteners that withstand the test of time and extreme conditions. Self-locking stainless steel cable ties deliver exceptional durability and longevity. Their inherent material strength provides a robust solution for securing cables and components. You can rely on their superior tensile strength, which far exceeds that of plastic alternatives.
Consider the impressive tensile strength ratings for these ties:
| Type of Cable Tie | Tensile Strength (lbs) |
|---|---|
| Standard | 200 |
| Heavy-duty | 300 |
| General | 200 to 900 |
| Upon request | 350 |
This high tensile strength ensures your installations remain secure even under significant stress or vibration. You will find that these ties maintain their integrity where plastic ties would fail. In outdoor industrial settings, self-locking stainless steel cable ties typically last between 10 and 30 years. Even in harsh environments, these ties regularly exceed a 10-year lifespan. This significantly outperforms plastic alternatives, which often become brittle and crack within months or a few years.
Versatility Across Demanding Environments for Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You operate in diverse and challenging environments. Self-locking stainless steel cable ties offer remarkable versatility, performing reliably where other materials degrade. They excel in conditions ranging from extreme temperatures to corrosive chemical exposures.
These ties boast an impressive operating temperature range. You can use them from -80°C to +540°C (-112°F to 1000°F). They withstand temperatures exceeding 400°C, offering both high heat and corrosion resistance. This makes them ideal for applications in furnaces, engines, or refrigeration units.
Furthermore, their corrosion resistance is outstanding, especially in saltwater or chemical environments. Saltwater is particularly harsh, corroding and weakening standard materials. Saltwater-resistant cable ties specifically resist this corrosion. They provide a secure and lasting solution for managing cables and hoses in marine settings, ensuring safety and efficiency.
You can select different grades of stainless steel for specific corrosive challenges:
| Grade | Composition (Key) | Corrosion Resistance (Saltwater/Chemicals) | Suitability for Saltwater/Chemicals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel | Resists mild corrosion; unsuitable for strong acids or saltwater | Unsuitable for saltwater or strong acids; rusts within 6-12 months in saltwater |
| 316 Stainless Steel | 2-3% Molybdenum added | Superior resistance to salt spray and industrial chemicals (acids, alkalis) | Recommended for marine environments and industrial corrosive settings |
| 316L Stainless Steel | Low carbon content | Superior resistance; avoids intergranular corrosion | Recommended for deep-sea applications |
| 317 Stainless Steel | More Molybdenum than 316 | Extreme chemical resistance | Recommended for industrial corrosive settings (extreme chemical resistance) |
| 430 Stainless Steel | No nickel | Poor in humid or corrosive settings | Rarely used for critical applications in corrosive environments |
For marine and coastal environments, such as shipbuilding or offshore wind farms, Grade 316 stainless steel is essential. Grade 304 will rust within 6-12 months in these conditions. For deep-sea applications, you should use 316L to prevent intergranular corrosion. In industrial corrosive settings like chemical plants or refineries, Grade 316 or 317 stainless steel is recommended. These grades resist acids, alkalis, and solvents.
Cost-Effectiveness Through Reduced Maintenance with Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You seek solutions that offer long-term value. Self-locking stainless steel cable ties provide significant cost-effectiveness through reduced maintenance. Their extended lifespan minimizes the need for frequent replacements. This directly translates into savings on material costs and labor.
Consider the long-term financial benefits:
| Metric | Stainless Steel Cable Ties | Plastic Cable Ties |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Cost Reduction (over 10 years) | 92% less | N/A |
| Annual Replacements | 67% fewer | Higher |
| Inspection Frequency | 17% as often | Regular |
| Service Life | Over two decades | Degrade rapidly |
| Downtime Cost Avoidance | Significant | Higher risk of stoppages |
You experience fewer unexpected stoppages and less downtime. This avoids substantial costs, potentially saving hundreds of thousands of dollars per hour in critical operations. You invest once in a reliable solution, avoiding recurring expenses associated with inferior fasteners.
Ease of Installation and Enhanced Security
You need efficient installation processes without compromising security. Self-locking stainless steel cable ties offer both. Their design facilitates straightforward application while ensuring a robust and tamper-resistant hold.
To ensure optimal security during installation, you should use specific tools and techniques:
- Tensioning tool: This tool is essential for achieving the correct tightness. It prevents over-torquing, which can damage cables or deform objects.
- Cutting tool: You use this tool for trimming excess tie material. It ensures a clean and safe finish without leaving sharp edges.
- Protective gloves: You should wear these due to the potentially sharp edges of stainless steel ties.
You follow a clear step-by-step process for installation:
- Select the Right Cable Tie: Choose based on length, width, type, bundle size, environment, and exposure to chemicals or temperature.
- Bundle the Cables or Objects: Neatly align and bundle items. Avoid twisting or over-compression.
- Insert the Tie: Wrap the tie around the bundle. Feed the tail through the self-locking head, such as a ball-locking or snap-lock mechanism.
- Apply Tension with the Tool: Use a tensioning tool to pull the tie tight. This ensures consistent pressure. The tool should be compatible with the tie’s width. It often has a built-in cutoff function.
- Trim the Excess: If the tool does not auto-cut, manually trim the tail with a sharp cable tie cutter. Avoid jagged edges.
- Inspect the Tie: Verify the tie is secure. Ensure the bundle is firm and the locking mechanism is fully engaged. Check for and smooth any sharp edges.
A stainless steel cable tie tensioning tool is recommended for precise and consistent tightening. This specialized tool helps you achieve the correct tension without damaging cables or the tie itself. It prevents over-tightening. It allows for consistent and controlled tension application. It often features adjustable settings for different tie sizes and bundle requirements. The tool may also automatically cut the excess tail once the proper tension is reached. After installation, you inspect the tie to ensure proper tension and positioning. You verify the locking mechanism is fully engaged and secure.
Key Industries Driving the Demand for Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You now understand the superior performance of self-locking stainless steel cable ties. Many critical industries increasingly adopt these fasteners. They recognize the need for robust, reliable solutions in their demanding operational environments.
Energy Sector (Oil & Gas, Renewable Energy)
The energy sector relies heavily on durable fastening. In oil and gas, you use these ties for bundling and fixing electrical cables on drilling equipment. You also fasten pipelines carrying fluids, ensuring secure connections and preventing leaks. They organize and protect control cables on offshore platforms. For renewable energy, self-locking stainless steel cable ties are crucial. Their secure locking mechanism prevents slippage, ensuring a firm grip on cables even under mechanical stress. You find them in solar farms, wind turbines, and hydroelectric plants. They mount solar cables, secure turbine blade sensors, and anchor hydro-power components.
Marine and Shipbuilding
Marine and shipbuilding environments demand extreme corrosion resistance. You need fasteners that withstand constant exposure to saltwater and harsh weather. Stainless steel cable ties, especially Grade 316, provide this essential protection. They secure critical wiring and components on vessels and offshore structures, ensuring long-term reliability.
Automotive and Transportation
In automotive and transportation, you face constant vibration, extreme temperatures, and potential chemical exposure. These ties secure wiring harnesses, exhaust systems, and other critical components. They maintain integrity under dynamic loads, preventing failures that could compromise safety and performance.
Construction and Infrastructure
Construction projects require robust solutions for organization and safety. You use self-locking stainless steel cable ties for bundling and securing cables, wires, and other items. Their ratchet mechanism prevents loosening, making them tamper-resistant. This contributes to an organized cable management system, enhancing overall project safety and efficiency.
Telecommunications and Data Centers
Telecommunications and data centers demand reliable cable management. You use stainless steel cable ties due to their resistance to environmental factors. This ensures reliable communication networks and long-term performance. They provide enhanced security, reducing the risk of cable damage and unauthorized access. You also achieve improved aesthetics and longevity, making them a cost-effective choice for sustainable cable management.
Choosing the Right Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties for Your Needs
You understand the power of self-locking stainless steel cable ties. Now, you must select the correct type for your specific application. Making the right choice ensures optimal performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness.
Material Grades: 304 vs. 316 Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You often face a choice between 304 and 316 stainless steel. Each grade offers distinct advantages. 304 stainless steel cable ties suit most general applications. They provide a strong, durable method for bundling and securing items in various settings. This includes indoor and outdoor environments where exposure to harsh chemicals or saltwater is minimal.
However, 316 stainless steel includes 2% molybdenum. This enhances its corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides like sea salt and pool chemicals. You should choose 316 stainless steel cable ties for marine environments, chemical processing equipment, and other high-corrosion areas. For instance, 316 is essential for offshore oil platforms, drilling platforms, and chemical plants. It resists a broad spectrum of chemicals and solvents. Field tests show 316L stainless steel withstands saltwater exposure for over a year. It also performs better than 304 in salt spray tests within chemical facilities.
Coated vs. Uncoated Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You also decide between coated and uncoated ties. Coated self-locking stainless steel cable ties offer significant advantages. A protective plastic coating, such as PVC or epoxy resin, prevents electrical problems and damage to held items. This coating protects against sharp edges and provides better grip for safer installation. For electrical installations with heavy power cables, a coated tie prevents reactions between bare steel and galvanized surfaces. The coating also provides superior protection against harsh environments and chemicals.
You generally prefer uncoated self-locking stainless steel cable ties for indoor applications. They are also a more suitable choice when cost-effectiveness is a significant factor. The absence of a coating is sufficient for indoor use. Here, additional protection against environmental influences or for user/cable protection from sharp edges is not typically required.
Size and Tensile Strength Considerations for Self-Locking Stainless Steel Cable Ties
You must consider the size and tensile strength of the ties. Match these specifications to your application’s requirements. Ensure the tie can securely hold the bundle without over-tightening or failing under load.
You now understand the revolution. Self-locking stainless steel cable ties offer superior durability, unmatched versatility, and long-term cost-effectiveness. They represent a necessary upgrade for reliable, high-performance fastening. You need these ties for increasingly demanding industrial environments, ensuring secure and lasting solutions.
FAQ
Why should you choose self-locking stainless steel cable ties over plastic?
You choose stainless steel for unmatched durability. It resists extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and corrosion. Plastic ties quickly fail in harsh industrial environments.
Can you use these ties in marine or outdoor settings?
Yes, you can. Stainless steel ties, especially Grade 316, excel outdoors. They resist saltwater and harsh weather, ensuring long-term security for your installations.
Do you need special tools to install self-locking stainless steel cable ties?
You should use a tensioning tool. It ensures correct tightness and prevents damage. This tool helps you achieve a secure, consistent hold every time.
Post time: Nov-27-2025